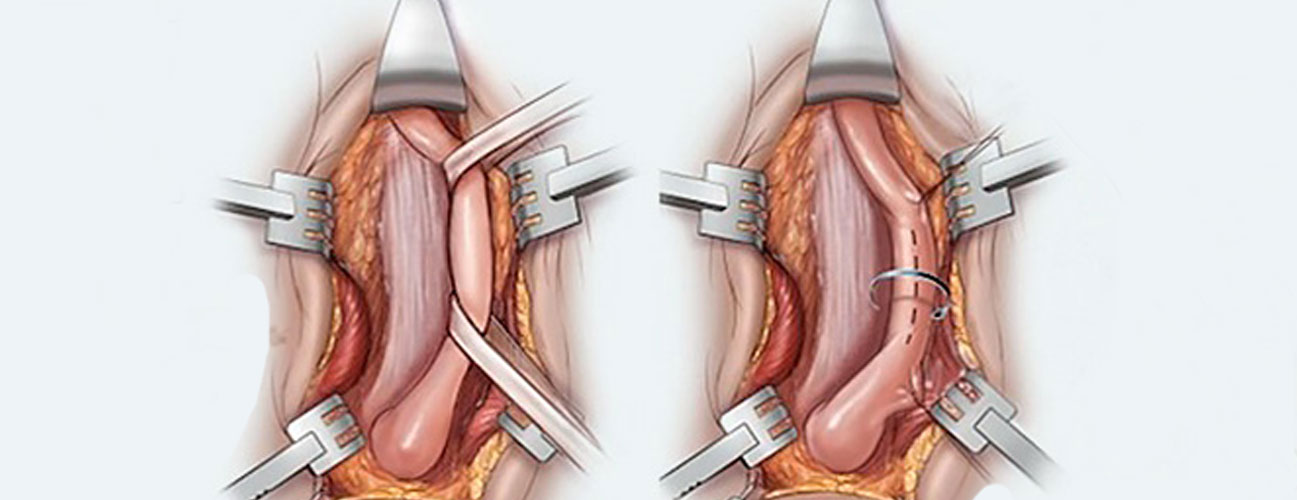
Urethroplasty is a surgical procedure aimed at repairing or reconstructing the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. This surgery is typically performed to treat urethral strictures, which are narrowings or blockages in the urethra caused by scar tissue. These strictures can result from trauma, infections, surgeries, or medical conditions such as lichen sclerosus. Urethroplasty is considered a definitive treatment, offering a high success rate compared to other interventions like dilations or urethrotomy.
There are different types of urethroplasty procedures, and the choice depends on the severity, length, and location of the stricture. An anastomotic urethroplasty involves removing the narrowed segment of the urethra and reconnecting the healthy ends. In contrast, substitution urethroplasty uses tissue grafts, often harvested from the inside of the cheek (buccal mucosa), to replace or augment the affected area. These techniques allow surgeons to tailor the procedure to the patient’s specific condition, ensuring optimal outcomes.
The surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia and may require a hospital stay, depending on the complexity of the procedure. After surgery, a catheter is typically placed in the urethra to allow for healing and ensure proper urine flow. The recovery period can vary, with most patients resuming normal activities within a few weeks, although strenuous activities may need to be avoided for a longer duration. Follow-up visits are crucial to monitor healing and detect any complications early.
Urethroplasty has a high success rate, often exceeding 85-90%, and significantly improves the quality of life for patients suffering from urethral strictures. However, like any surgery, it carries potential risks, including infection, bleeding, or recurrence of the stricture. Long-term outcomes are generally favorable, but periodic evaluations may be necessary to ensure the urethra remains unobstructed.
Overall, urethroplasty is a highly effective treatment option for urethral strictures, offering lasting relief and improved urinary function. Patients experiencing symptoms such as difficulty urinating, frequent infections, or urinary retention should consult a urologist to determine if urethroplasty is an appropriate solution. A thorough evaluation and discussion with the surgeon can help patients make informed decisions about their care.