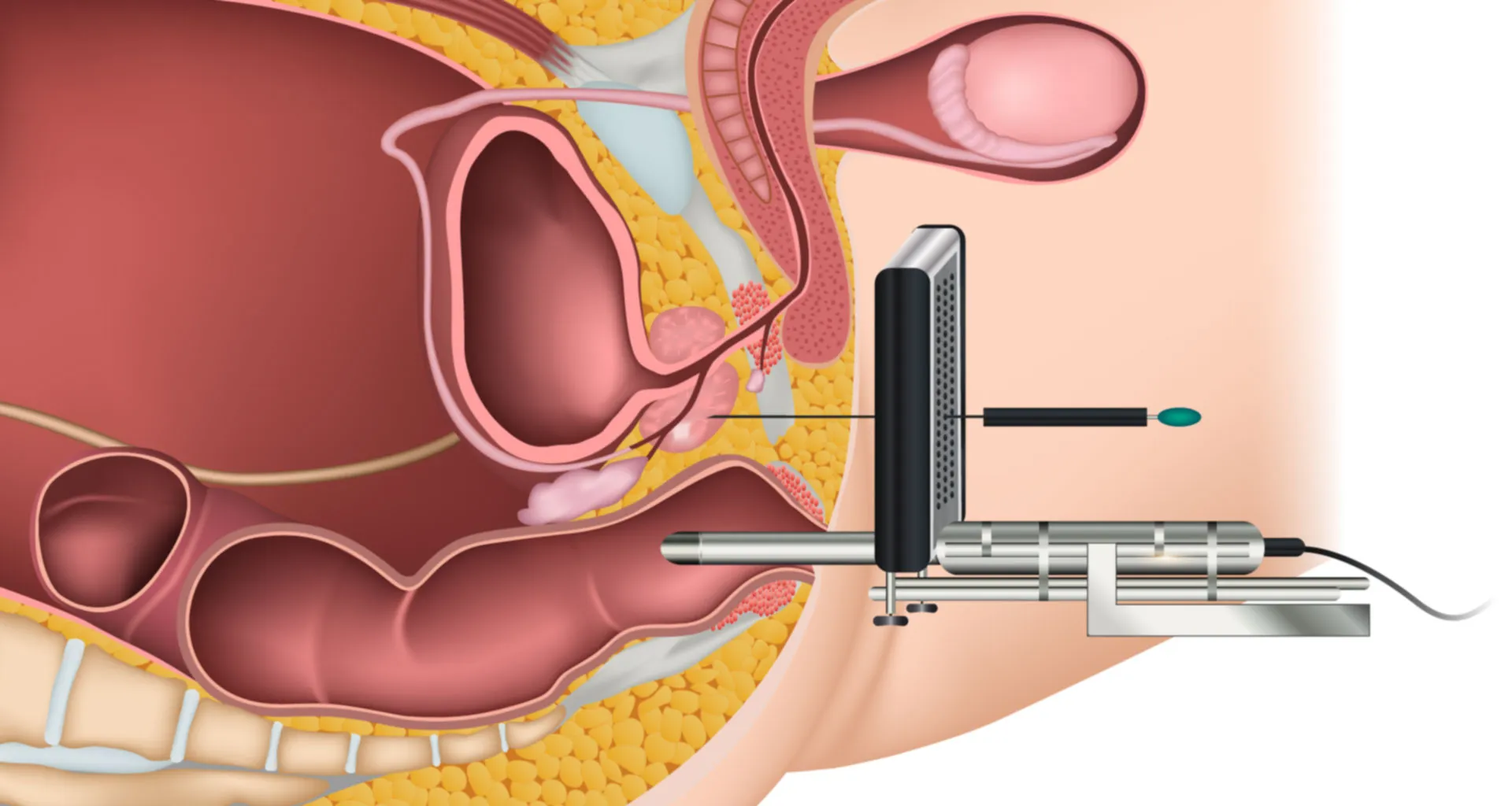
A prostate biopsy is a medical procedure used to obtain small samples of prostate tissue for examination under a microscope. It is typically performed to diagnose or rule out prostate cancer in men with elevated prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels or abnormalities detected during a digital rectal exam (DRE). The procedure helps pathologists determine if cancer cells are present, their grade, and the extent of the disease, guiding further treatment or management decisions.
The most common method of performing a prostate biopsy is the transrectal ultrasound-guided (TRUS) approach. During this procedure, a thin ultrasound probe is inserted into the rectum to visualize the prostate gland. Using this imaging as a guide, the physician inserts a thin needle through the rectal wall to collect tissue samples from different areas of the prostate. Other approaches, such as transperineal biopsy, involve accessing the prostate through the perineum (the skin between the scrotum and anus), offering an alternative for patients with specific conditions or preferences.
The biopsy is usually performed under local anesthesia and is a relatively quick outpatient procedure, often lasting less than 30 minutes. After the biopsy, patients may experience mild discomfort, rectal bleeding, blood in the urine or semen, or temporary difficulty urinating. These side effects are generally short-lived and resolve without intervention. However, rare complications such as infection or prolonged bleeding may occur, necessitating medical attention.
The tissue samples obtained during the biopsy are analyzed by a pathologist to check for the presence of cancer cells. If cancer is detected, the biopsy results will include information about the Gleason score, which indicates the aggressiveness of the cancer. This information is critical in determining the stage of the disease and planning appropriate treatment options, which may range from active surveillance to surgery, radiation, or other therapies.
A prostate biopsy is a vital diagnostic tool for evaluating prostate health and detecting cancer early. Men with abnormal PSA levels, DRE findings, or other risk factors for prostate cancer should consult a urologist to discuss the need for a biopsy. Understanding the procedure, potential risks, and implications of the results can help patients make informed decisions about their prostate health and overall well-being.